Infographic
Confronting the life science diversity problem
Using technology to address issues of diversity and inclusion across the drug development lifecycle.
Only 32%
of organizations have outreach programs to encourage a more culturally/ethnically diverse workforce. – INFORMA CONNECT


Women’s representation remains low in clinical trials, particularly in phase I trials (≈22%). – BMJ
Less than 10% of cancer patients enrolled in clinical trials are racial or ethnic minorities. – THE SIDNEY KIMMEL COMPREHENSIVE CANCER CENTER
Improving diversity and inclusion in life science is more than just the right thing to do – there’s also a sound business imperative to do so.
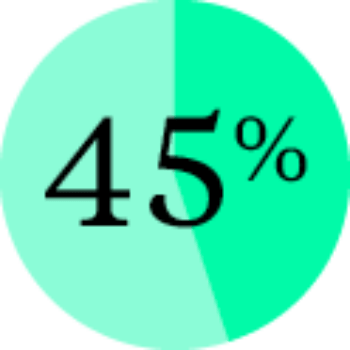
Companies with above-average diversity produced a greater proportion of revenue from innovation (45% of total). – FORBES
In 2019, top-quartile companies [for ethnic diversity] outperformed those in the fourth quartile by 36% in profitability. – MCKINSEY
Diversity in clinical trial recruitment is a significant shortfall for life science companies, with a number of barriers to participation excluding underserved communities.
“53% of non-Hispanic white participants said that they trusted their health professionals ‘a lot,’ compared with 37% for non-Hispanic black participants and 36% for Hispanic participants.”
Technologies including artificial intelligence, network analytics, social listening, and virtual asynchronous engagement are helping to remove these barriers to trial participation.
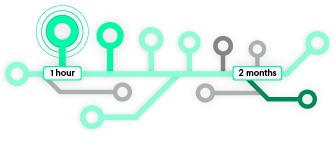
An AI-enhanced trial at Cedars-Sinai identified 16 candidates in one hour, while a human-based approach found two people in six months.
“Decentralization broaden trial access to reach a larger number and potentially a more diverse pool of patients.”
An AI-enhanced trial at Cedars-Sinai identified 16 candidates in one hour, while a human-based approach found two people in six months.
Expert identification is another area where life science falls short, with many companies continuing to rely on the same pool of established KOLs.

Only 30% of global researchers are women.

64% of members considered speaker diversity a necessity…

…while only 46% agreed that their conferences had achieved it.
Network analytics can reveal the ‘invisible college’ within a disease community, based on true network influence rather than volume of activity.
Even when diversity has been achieved, hierarchy bias within the life science sector prevents all voices from being heard.

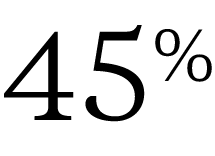
of female business leaders say it’s difficult for women to speak up in virtual meetings.
– CATALYST
By anonymizing participants through anonymous questions, asynchronous virtual engagement can ensure that every voice is heard – effectively eliminating hierarchy bias.

“Anonymous survey methods appear to promote greater disclosure of sensitive or stigmatizing information compared to non-anonymous methods.”
“Diverse groups who are visually anonymous will produce more creative results than homogeneous groups or groups who are diverse but not visually anonymous.”
While technology isn’t a magic bullet, it can effectively support life science companies’ existing diversity and inclusion efforts to smooth the way for a more equitable, representative future. Discover the four technologies supporting life science D&I efforts in our e-book: Confronting the Life Science Diversity Problem.



